Loyola University’s Center for Innovation and Collaborative Learning
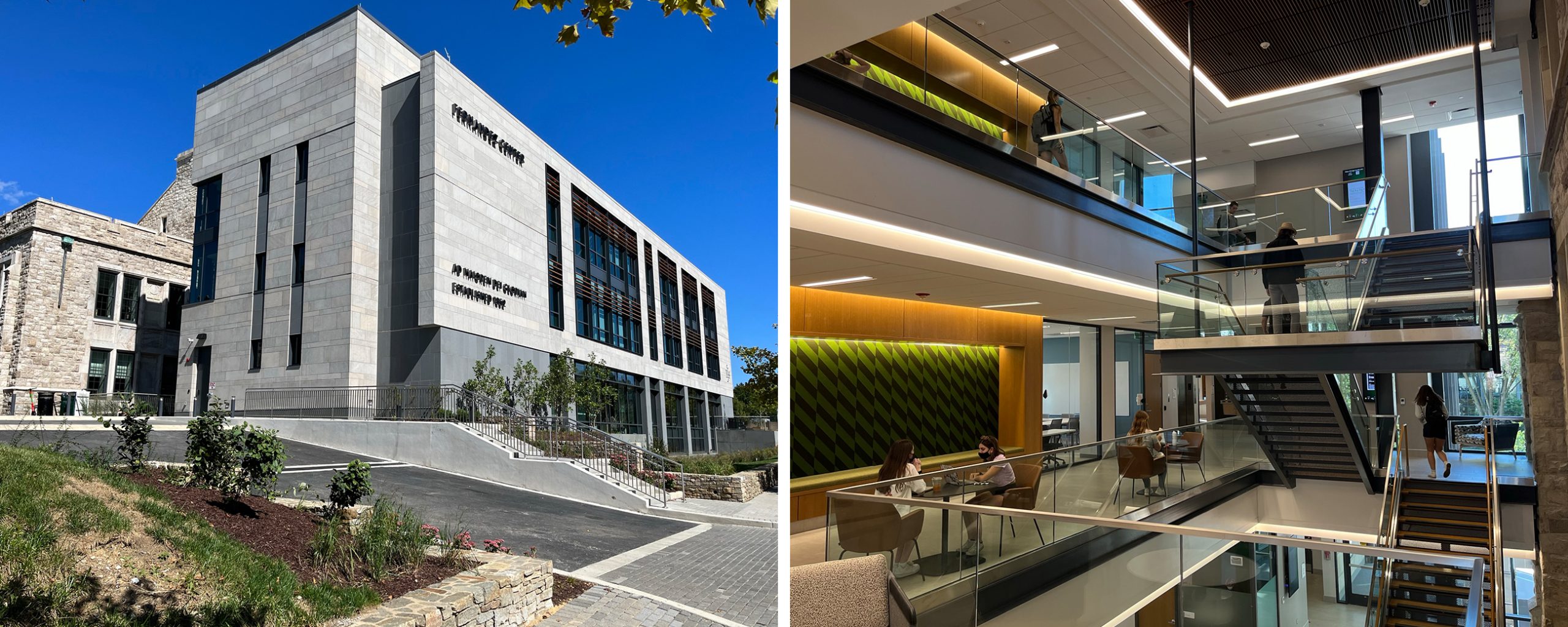
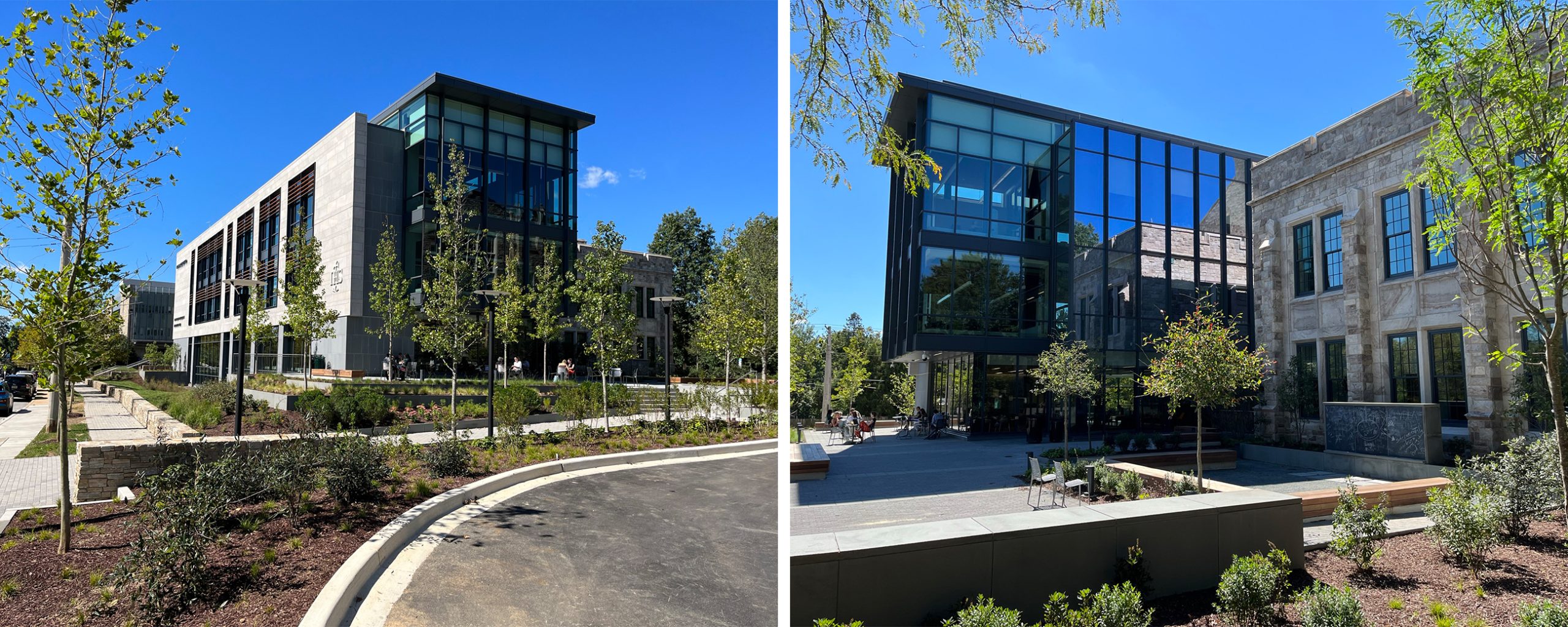
Originally constructed on the Campus of Loyola University in 1992, Beatty Hall was transformed into The Fernandez Center for Innovation and Collaborative Learning through a substantial renovation and expansion project led by Shepley Bulfinch. The newly renovated building serves as the central hub for the campus community and features active learning classrooms, creative labs and innovation spaces, career centers, interactive lounges, and a café. In addition, the building also features a four-story atrium to enhance the communication amongst all floors in the building.
Code Red Consultants was responsible for developing and presenting the building’s code compliance approach to the City of Baltimore’s Building and Fire Departments. Code Red Consultants’ services included building, fire, and accessibility code consulting as well as performance-based design analysis of the atrium smoke control system using a computational fluid dynamics computer model.
Location
Baltimore, Maryland
Size
61,600 GSF
Cost
$40 million
Completion
Winter 2021
Photography Credit
Shepley Bulfinch
Loyola University’s Center for Innovation and Collaborative Learning
Originally constructed on the Campus of Loyola University in 1992, Beatty Hall was transformed into The Fernandez Center for Innovation and Collaborative Learning through a substantial renovation and expansion project led by Shepley Bulfinch. The newly renovated building serves as the central hub for the campus community and features active learning classrooms, creative labs and innovation spaces, career centers, interactive lounges, and a café. In addition, the building also features a four-story atrium to enhance the communication amongst all floors in the building.
Code Red Consultants was responsible for developing and presenting the building’s code compliance approach to the City of Baltimore’s Building and Fire Departments. Code Red Consultants’ services included building, fire, and accessibility code consulting as well as performance-based design analysis of the atrium smoke control system using a computational fluid dynamics computer model.